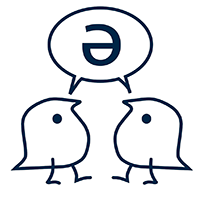
At (conjunction)
The conjunction at in spoken language is used as subordinating conjunction in the beginning of a subordinate clause, connecting it to a main clause just like in written language. In spoken language at is realized only with an a-vowel [a]. Below is an example of this realization, where the speaker Asta (AST) states that everybody with a job pays almost the highest tax rates.

Here a (’that’) connects the main clause jamen det jo sådan (‘well it is so’) with the subordinate clause alle betaler næsten topskat (‘everybody pays almost the highest tax rates’). The at (‘that’) from written language is transcribed with the vowel a, and the [a]-form is the common way of expressing the subordinating conjunction.
There are special cases in which an [ad]-form occurs, which resembles the written form, and which has the same subordinating function as the a-form. [ad] occurs in connection with hesitation markers in utterances and is transcribed at.
Below is an example from a police interrogation where a police officer is interrogating a young man.

In this case [ad] occurs in line 01 right before a pause, which in spoken language is a hesitation marker
[ad] also occurs before the hesitation marker øh. In the example below Annette (ANN) replies to a question regarding why and for whom she is making recordings.
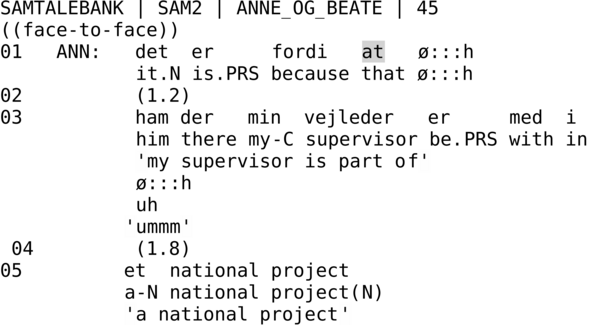
Here [ad] occurs in her explanatory subordinate clause before ø::h in line 45. In addition [ad] can be used to emphasize the content of a subordinate clause. In the following example Lis (LIS) is telling that her grandmother bought a piano on an instalment plan that she couldn’t afford, because she wanted her girls to learn how to play.

Here Lis is emphasizing the subordinate clause, which is that her grandmother did it – she bought a piano in spite of the fact she couldn’t afford it, because she wanted her daughters to learn how to play.
Sources and further readings
Bruun (2018) is a thorough description of og (’and’)/at (’that’).
Relevant entries
The Building Blocks of Talk-in-interaction > Word classes/parts of speech > Conjunctions